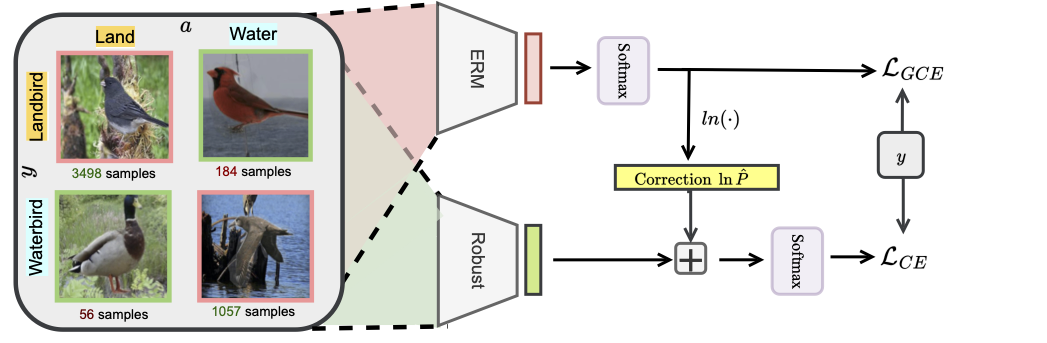
Avoiding Spurious Correlations via Logit Correction
We propose the logit correction (LC) loss, a simple yet effective improvement on the softmax cross-entropy loss, to correct the sample logit. We demonstrate that minimizing the LC loss is equivalent to maximizing the group-balanced accuracy, so the proposed LC could mitigate the negative impacts of spurious correlations.
Deep Probability Estimation
ICML 2022
Reliable probability estimation is of crucial importance in many real-world applications where there is inherent (aleatoric) uncertainty. Probabilityestimation models are trained on observed outcomes (e.g. whether it has rained or not, or whether a patient has died or not), because the ground-truth probabilities of the events of interest are typically unknown. The problem is therefore analogous to binary classification, with the difference that the objective is to estimate probabilities rather than predicting the specific outcome. This work investigates probability estimation from high-dimensional data using deep neural networks.
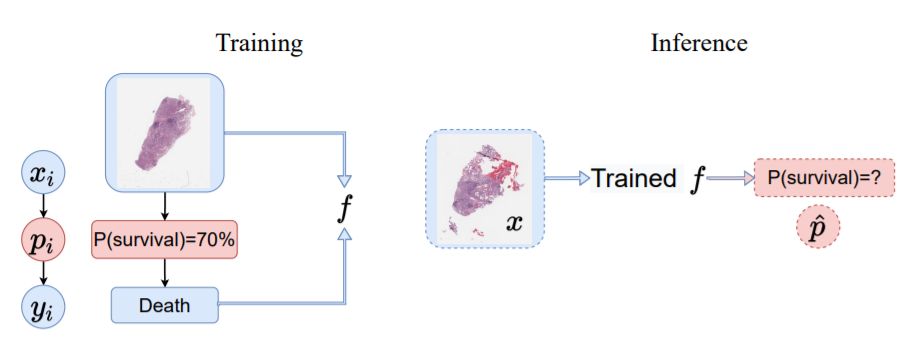
(e.g. death or survival in cancer patients) in the training set is randomly generated from a latent unobserved probability
associated to the corresponding data
(e.g. histopathology images).Training (left): Only
and
can be used for training, because
is not observed. Inference (right): Given new data
, the trained network
produces a probability estimate
in [0,1].
Adaptive Early-Learning Correction for Semantic Segmentation
CVPR 2022 Oral
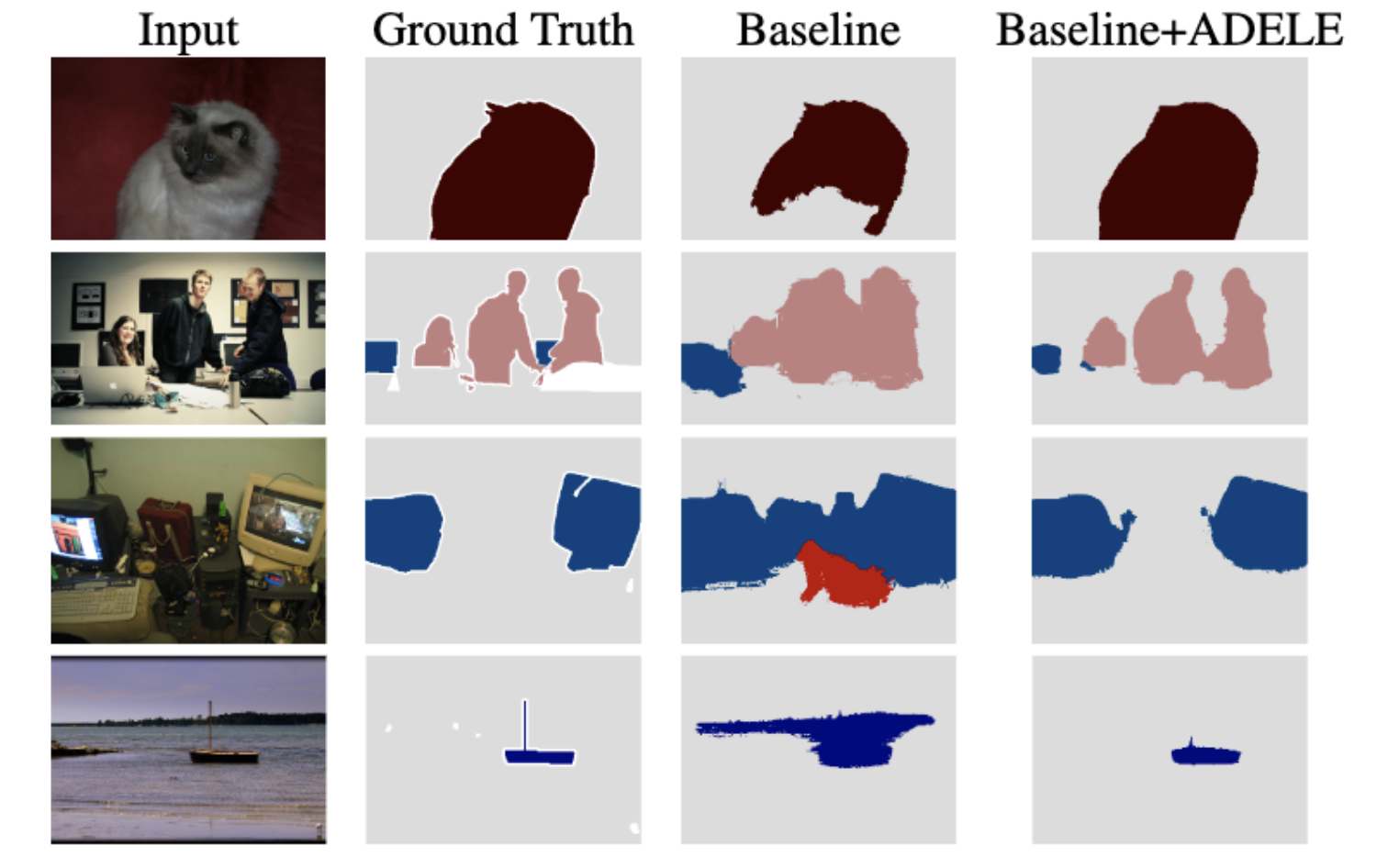
Deep learning in the presence of noisy annotations has been studied extensively in classification, but much less in segmentation tasks. In this project, we study the learning dynamics of deep segmentation networks trained on inaccurately-annotated data and propose a new method for semantic segmentation ADaptive Early-Learning corrEction (ADELE).
Early-learning Regularization Prevents Memorization of Noisy Labels
NeurIPS 2020
We propose a novel framework to perform classification via deep learning in the presence of noisy annotations. When trained on noisy labels, deep neural networks have been observed to first fit the training data with clean labels during an early learning phase, before eventually memorizing the examples with false labels. Our technique exploits the progress of the early learning phase via regularization to perform classification from noisy labels.
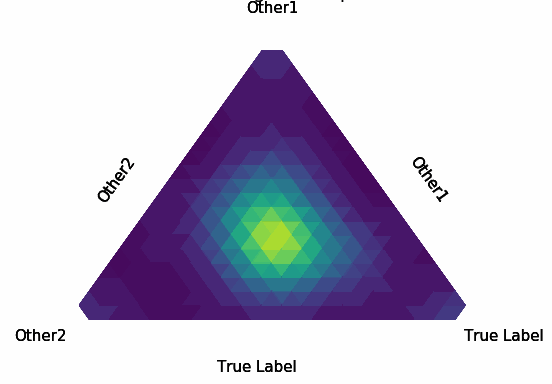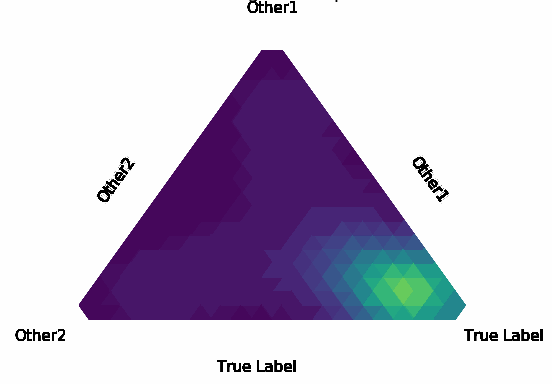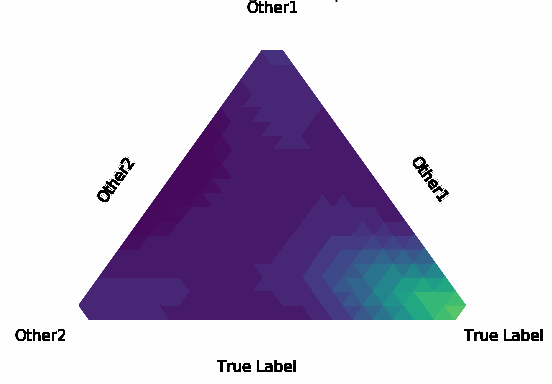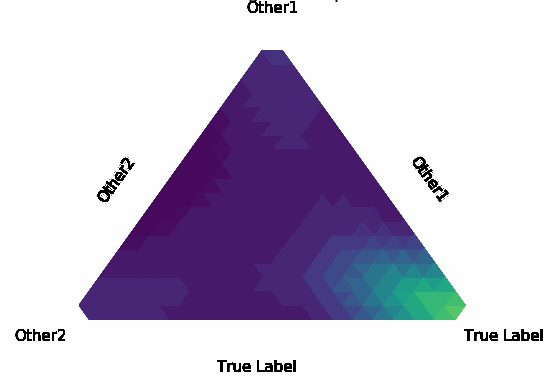
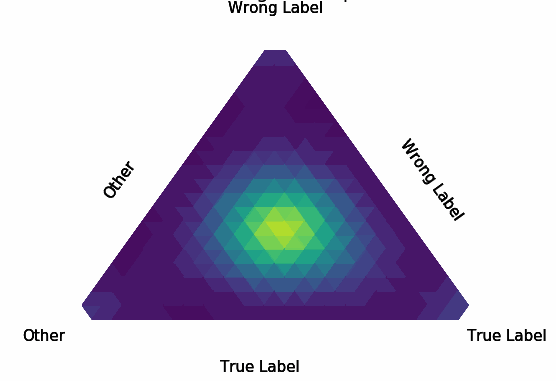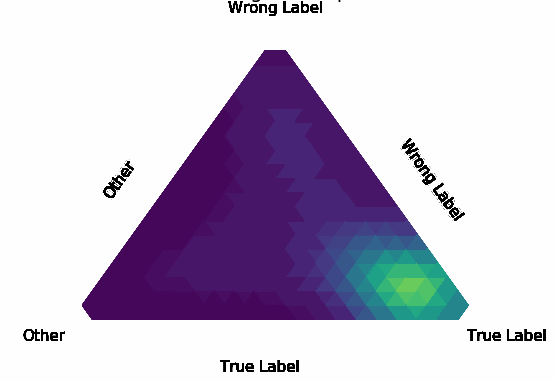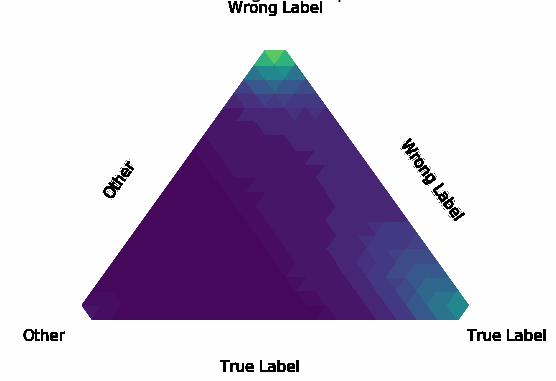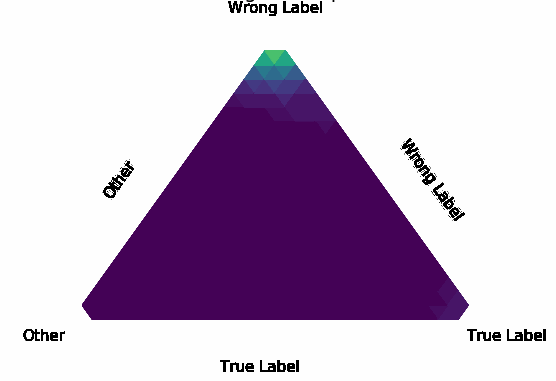
Normalization Layer Improve Robustness of Convolutional Neural Networks
NeurIPS 2021
Normalization techniques have become a basic component in modern convolutional neural networks (ConvNets). In particular, many recent works demonstrate that promoting the orthogonality of the weights helps train deep models and improve robustness. For ConvNets, most existing methods are based on penalizing or normalizing weight matrices derived from concatenating or flattening the convolutional kernels. These methods often destroy or ignore the benign convolutional structure of the kernels; therefore, they are often expensive or impractical for deep ConvNets. In contrast, we introduce a simple and efficient Convolutional Normalization (ConvNorm) method that can fully exploit the convolutional structure in the Fourier domain and serve as a simple plug-and-play module to be conveniently incorporated into any ConvNets.
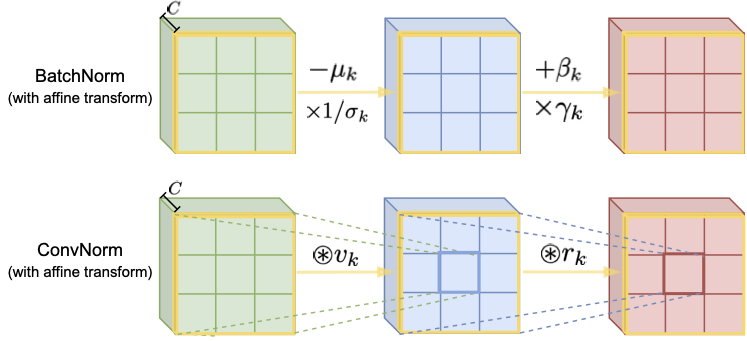
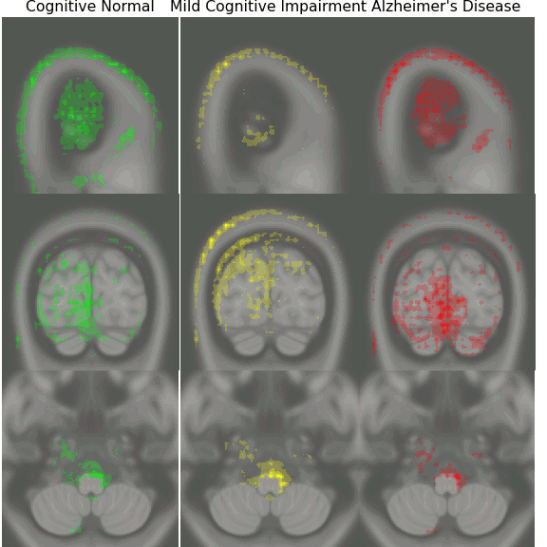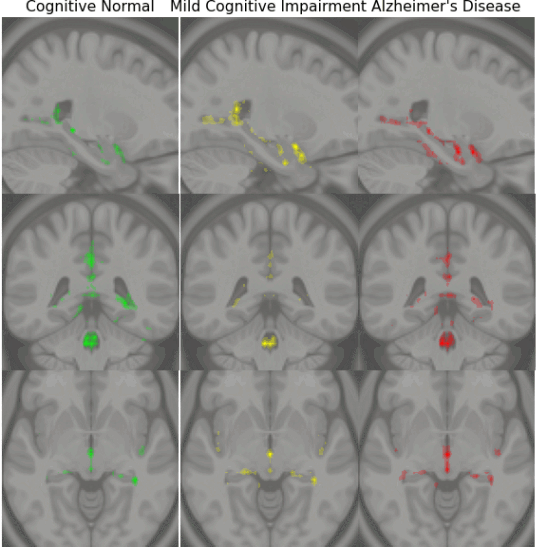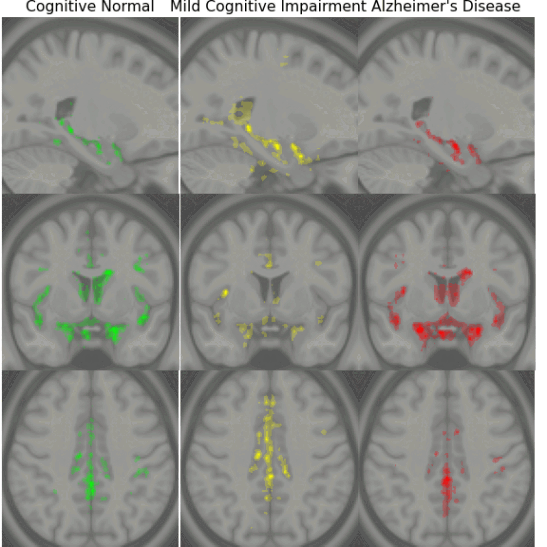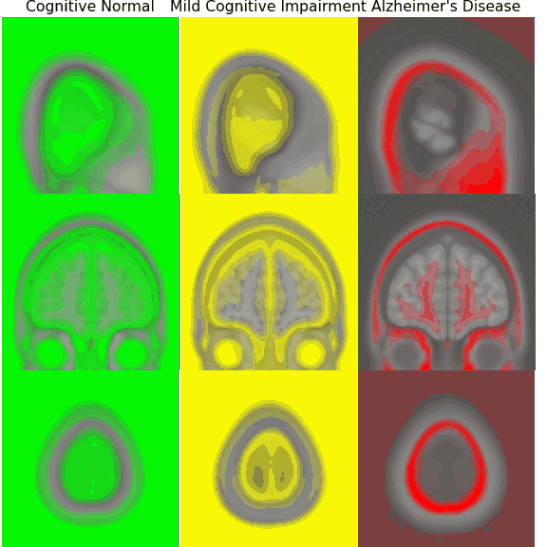
Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease with Convoltuional Neural Networks
Nature Scientific Reports
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease plays a pivotal role in patient care and clinical trials. In this study, we have developed a new approach based on 3D deep convolutional neural networks to accurately differentiate mild Alzheimer’s disease dementia from mild cognitive impairment and cognitively normal individuals using structural MRIs. For comparison, we have built a reference model based on the volumes and thickness of previously reported brain regions that are known to be implicated in disease progression. We validate both models on an internal held-out cohort from The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and on an external independent cohort from The National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC).